Dates in Diabetic Diet
- All About Dates Dates in Diet
- October 28, 2021
- 9 minutes read
Diet Description
In order to manage diabetes or pre-diabetes, choosing the right food is very important. A diet recommended for people with diabetes is very similar to a standard, healthy diet. The diabetic diet food list includes nutrient-rich foods. These include fruits and non-starchy vegetables. Low glycemic index foods and healthy fats are also good for their diet.
One way to manage blood sugar is by counting carbohydrates. Keeping track of them is very important. You must try spreading out the amount of carbohydrates eaten throughout the day. This will lead to success in using this method. Tracking carbohydrates can be done by reading nutrition labels. You may also try looking up the carbohydrate content of foods. Everyone has different needs. Therefore, working with a Registered Dietitian or Certified Diabetes Educator will be beneficial to learn carb counting. They will also help you determine how many carbohydrates you should have daily.
Building a plate is an easier method to manage blood sugar levels. It is also recommended by the American Diabetic Association. Start by filling half of your plate with non-starchy vegetables. One-quarter of the remaining plate will be a lean protein source, like fish, poultry, or tofu. The last quarter of the plate is left for carbohydrates. This may include grains, potatoes, or other starchy vegetables. Choose an unsweetened beverage or water to go with your meals.
The last part of this diet is having regular meal times. Eating moderate amounts during set meal times will help normalize blood sugar. This can look like planning three regular meals a day. You may also incorporate healthy snacks between meals, if necessary.
Diet Purpose
There are a couple of goals to keep in mind when following a diabetic diet. This includes: managing your blood sugar levels and losing weight. These goals can be easily met! All you need to do is eat moderate amounts of most nutrient-dense foods. Eating excess amounts of carbs will cause your blood sugar to rise. By following a diabetic diet, your body will be able to better process sugars. You’ll also utilize insulin more effectively.
Insulin is a hormone that carries sugars in the blood around the body. With diabetes, the body begins to lose the ability to properly use or produce insulin. This can lead to hyperglycemia. Hyperglycemia means that there is extra sugar in the blood. These sugars are not being used due to inadequate insulin. Uncontrolled, high blood sugar is very dangerous. Therefore, it should be addressed by a doctor immediately.
Being physically active can play a role in a healthy lifestyle. This is especially important when following a diabetic diet. It can also help with weight loss. This will make it easier to maintain blood sugar levels.
What to Eat
Fruits and Vegetables
Healthy carbohydrates like fruits make great snacks. You may also have non-starchy vegetables as an addition to meals. They are also high in fiber, which is great for people following a diabetic diet. Fiber slows down carbohydrate digestion. It also helps stabilize blood sugar. Eating foods higher in fiber may even contribute to weight loss!
Non-starchy vegetables are low in carbohydrates and high in fiber. This means this kind of veggie can be enjoyed freely! They actually have a small impact on blood sugar levels. Think leafy greens, asparagus, and brussels sprouts. You may also try out cauliflower, peppers, tomatoes, and so many more!
Low Glycemic Index Foods
The glycemic index of foods measures how much a food raises blood sugar in the body after it’s eaten. This is otherwise known as GI. As a general rule, foods with mostly carbohydrates will increase blood sugar more. They will also have a higher GI. Foods with a low glycemic index have a small impact on blood sugar. This is why they’re among the best foods for a diabetic diet.
Diabetic Diet Grocery Shopping List:
- old fashioned or steel-cut oats
- fruits: apples, apricots, berries, cherries, grapefruit, peaches, pears, prunes, plums, tangerine, and tomato juice
- beans and legumes, soy products
- non-starchy vegetables
- grains: barley, rye, wild rice, wheat
- nuts and seeds
- lean meats: skinless poultry, eggs, fish,
- milk: unsweetened plant-based milk, low-fat cheese, and milk
Healthy Fats
Healthy fats like oily fish, olive oil, and avocado are some recommended foods. You may also have nuts and seeds to replace sources of saturated or trans fats in the diet. Healthy fats play a role in heart health and lowering cholesterol. This may be helpful for maintaining diabetes. However, these foods should still be consumed in moderation because they are high in fats.
Dates in a Low-Cholesterol Diet
Dates are known for their sweet flavor. This is mostly because of their high carbohydrate content. Dates may be higher in carbs. However, they are also full of fiber, letting them offer a low to medium glycemic index. Because of this, dates consumed in small quantities should not upset blood sugar stability.
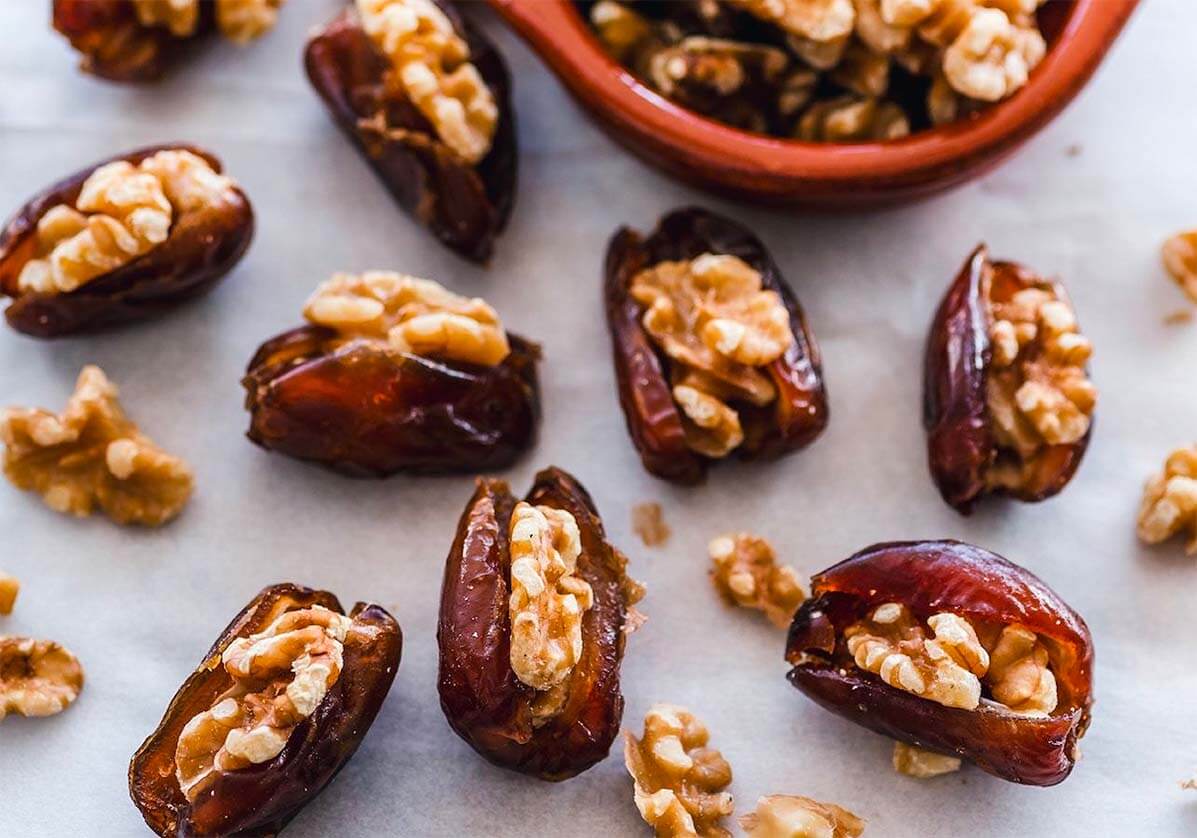
Dates eaten in small portions would make a satisfying snack on a diabetic diet. We recommend pairing dates with a protein and/or fat source. This includes nuts and seeds. Eating them together will help you stay fuller for longer. It will also lead to slow absorption of carbohydrates.
What to Avoid
High GI Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates with a high glycemic index should be avoided. This is especially true for those sourced from refined sugars and processed foods. They are not nutrient-dense foods, which means they are empty calories. They can also cause blood sugar spikes. This type of food includes candies and sweetened beverages. We also recommend against eating a lot of packaged snacks, desserts, etc.
Some vegetables may not be good for those with diabetes. Starchy vegetables have a high GI. Therefore, they should only be eaten in small quantities. Even though they are technically vegetables, they have a high carbohydrate content. This can then cause a sugar spike. Some starchy vegetables include potatoes, corn, and winter squash.
Cholesterol, Saturated, and Trans Fats
Having diabetes can increase the risk of stroke and heart disease. Following a heart-healthy diet is key in preventing these health conditions. We recommend reducing your intake of cholesterol, saturated and trans fats. Red meat, poultry with skin, eggs, and other animal products also contain significant amounts of cholesterol and saturated fats. Trans fats, on the other hand, can be found in baked goods and other packaged goods.
Conclusion
Following a diabetic diet is very similar to a standard diet. There is just an emphasis on eating nutrient-rich foods. This will help maintain blood sugar levels. Two goals of this diet are preventing blood sugar spikes and losing weight. This can be achieved in a variety of ways. We recommend focusing on foods like fruits and non-starchy vegetables. You may also eat low glycemic index foods and healthy fats. We also recommend against eating foods with a high glycemic index or food choices that are high in saturated fat and cholesterol. You may eventually need help transitioning to a diabetic diet. In that case, we recommend working with a Registered Dietitian or a Certified Diabetes Educator. They can be a very valuable resource.